- December 12, 2024
- Posted by: admin
- Category: BitCoin, Blockchain, Cryptocurrency, Investments


The post What is Chain Abstraction? A Way to Simplify Blockchain appeared first on Coinpedia Fintech News
Chain Abstraction is one of the rising crypto narratives as it simplifies on-chain interactions, heading towards mass blockchain adoption.
Interacting with blockchain can feel complex and overwhelming for those new to crypto. Without Chain Abstraction, users have to manage their wallets manually, select the right blockchain, pay gas fees, and many more. The complexity involved can intimidate beginners, which is why Chain Abstraction was developed to simplify interactions and lower the barrier to web3 entry.
This guide will show you what Chain Abstraction is, why it matters, and the benefits offered to new crypto users. Let’s dive in!
1. The Problem Towards Mass Adoption
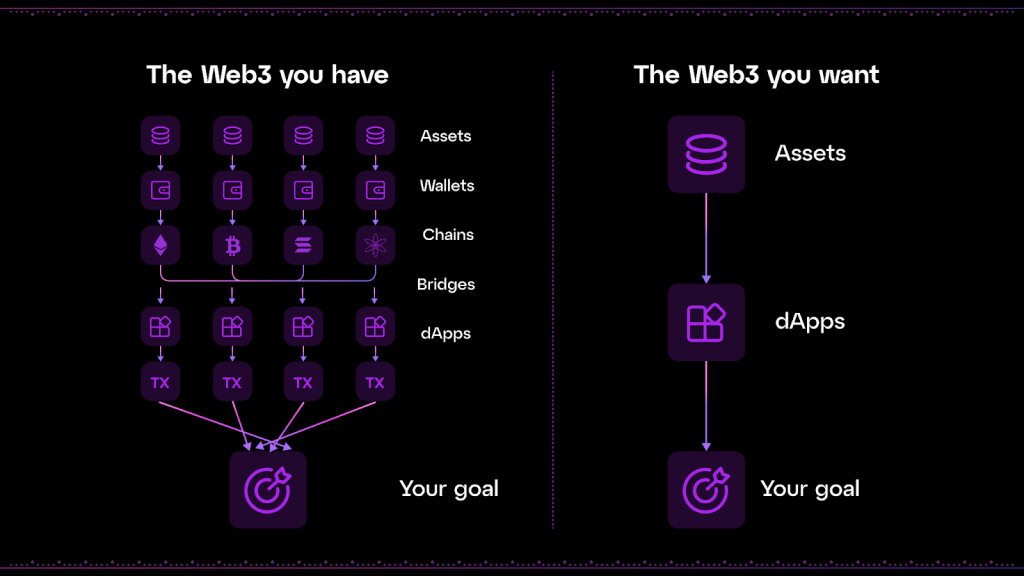
Web3 is fragmented beyond practical usability. Source: Particle Network
One of the main reasons crypto can be intimidating for new users is the fragmented user experience. As new chains, layers, and rollups launch and grow, users’ accounts and liquidity are growing. This creates endless problems for users and a clunky user experience.
Here are some main reasons
- Complex Onboarding Process: Many new users find blockchain interfaces too complicated to navigate.
- Fragmented User Experience: UX frictions remain a nagging problem for crypto users with hundreds of wallets, chains, and applications.
- Low Usage: Decentralized applications (dApp) developers often struggle to expand their user base due to complex blockchain interactions and the shortage of supported infrastructure.
- Capital Inefficiencies: Fragmentation has also brought along inefficiencies in Web3’s incentives and workings—some of them leading to the wastage of billions of dollars.
Chain Abstraction addresses this challenge head-on, and brings Web3 closer to Web2’s experience.
2. What is Chain Abstraction?
Chain Abstraction aims to abstract away the technical details of blockchain transactions, letting you use decentralized applications (dApps) without needing to understand the intricate workings of different networks.
By hiding the technical details of each blockchain, Chain Abstraction allows users and developers to interact with dApps effortlessly.
3. How Does Chain Abstraction Work?
In a multi-chain environment, the Permission, Solver, and Settlement layers work together to simplify and secure users’ experience.
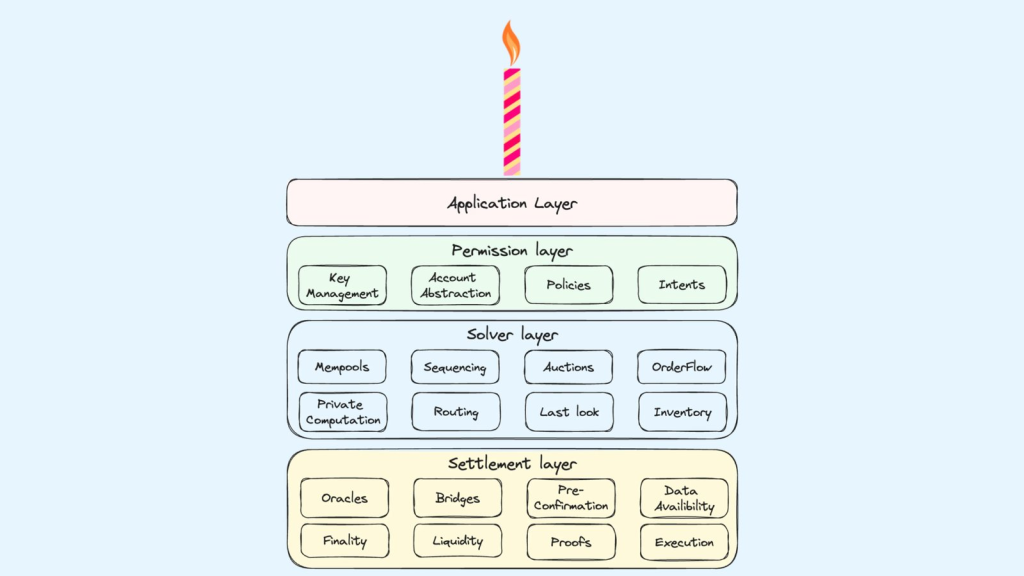
The CAKE framework for Chain Abstraction.
Permission Layer
When you connect your wallet to a dApp, you set an intent, like sending tokens to a wallet address or depositing funds to a smart contract on an Ethereum Layer 2. Instead of worrying about how it works on each chain, the Permission Layer just needs to know what you have and handle permissions to make it happen.
Solver Layer
Next, the Solver Layer works on calculating the best route for your transaction. It finds the ideal balance of fees, speed, and success rate, even accounting for the hiccups that can occur with cross-chain actions. This way, you get the best value without manual tweaking.
Settlement Layer
Once you approve with your private key, the Settlement Layer completes your transaction by moving assets to the target chain and finalizing your intent. Some protocols even provide their own liquidity to streamline this step, so you don’t have to bridge assets manually.
Together, these layers take the hassle out of multi-chain activity, letting you focus on what you want to achieve rather than the steps to get there.
4. Chain Abstraction’s Key Benefits
Chain Abstraction offers many advantages for new users, whether in cross-chain activities, token transfer, or exploring new applications.
- Seamless Experience: Chain Abstraction simplifies interactions with ecosystem dApps. This makes it easier for new users to participate in activities like yield farming or staking without getting bogged down by complex procedures.
- Cost Savings: By automatically selecting the chain with the lowest transaction fees, or supporting any tokens for gas payment, Chain Abstraction helps users optimize gas costs. This is especially useful when users are trading volatile assets or transferring cross-chain.
- Interoperability: Chain Abstraction allows users to access various networks and dApps from a single, unified interface. You can easily engage with different DeFi platforms or NFT marketplaces without the hassle of managing multiple wallets.
- Better Development: For developers, Chain Abstraction means creating apps that work across chains without limitations. They can leverage the best features from any blockchain, reaching more users and enhancing the ecosystem.
These benefits effectively enable users to engage more with the decentralized ecosystem, all while enhancing their overall experience in Web3.
5. Chain Abstraction in Action: Some Examples
There are some prominent projects that are working on Chain Abstraction.

The Chain Abstraction Market Map. Source: The Rollup
1. Particle Network
Particle Network is one of the major players in the Chain Abstraction landscape. Built on the Cosmos SDK, this network’s Chain Abstraction spans both EVM and non-EVM networks, meaning users from almost any chain can interact seamlessly. Their core features make this interoperability possible:
- Universal Accounts: A single account and balance across chains, so users don’t need to juggle multiple wallets.
- Universal Liquidity: Cross-chain atomic swaps make it easy to interact with multiple chains without holding assets on each.
- Universal Gas: Users can pay gas fees with any token, simplifying cross-chain transactions even further.
2. NEAR Protocol
NEAR Protocol takes a unique approach with multi-chain signatures, letting you use a single NEAR account to transact across NEAR, Ethereum, Avalanche, BNB Smart Chain, and Bitcoin
Imagine using one account for all these chains—no more switching wallets or managing different accounts. NEAR’s cross-contract calls allow a smart contract on one chain to trigger an action on another. Chain signatures are verified across chains, making seamless interactions possible without switching back and forth.
Embed Tweet: https://x.com/PinkBrains_io/status/1841040660067205381
3. Socket
Another builder in Chain Abstraction is Socket. It can be seen as a Chain Abstraction marketplace, where various actors are incentivized to provide developers and users with the most seamless and cost-efficient experience.
The Magic Account is one of the features built on Socket, offering the first look into chain abstraction. In detail, the Magic Account merges your balances across chains into a single account, so you can use your assets on any app, anywhere.
Embed Tweet: https://x.com/litocoen/status/1833581746946036028
Final Words
Although most projects in the area are still in the early phase, Chain Abstraction is set to change the way people interact with blockchain. By simplifying complex on-chain execution, optimizing costs, and improving user experience, it lowers the barriers to crypto adoption and makes the blockchain space more accessible to beginners.
